Pipeline Features¶
The Consistency module¶
The CosmoSIS standard library has a particularly helpful module called consistency, which is designed to translate automatically between different ways of expressing cosmological parameters.
For example, if your values file specifies both \(\Omega_m\) and \(h^2\) then it will calculate \(\omega_m \equiv \Omega_m h^2\) for you automatically.
Any sufficient choice of the parameters can be specified and the remainder will be determined.
To use this module, just include the module utility/consistency/consistency_interface.py at the start of a pipeline.
Pre- and post-scripts¶
CosmoSIS can automatically run a script before executing your pipeline; if the script returns an error code then the pipeline will not be run.
It can also run a script after the
You could use this feature to: - run a check before the pipeline to make sure some test result is as expected. - download some data that is needed for a pipeline. - postprocess results after the pipeline is complete and make some plots.
To use this feature, add lines in the [runtime] section of the parameter file:
[runtime]
pre_script=./my_pre_script.sh
post_script=./my_post_script.sh
Your scripts can be any executable. If the pre-script has a non-zero return value then the pipeline will not run.
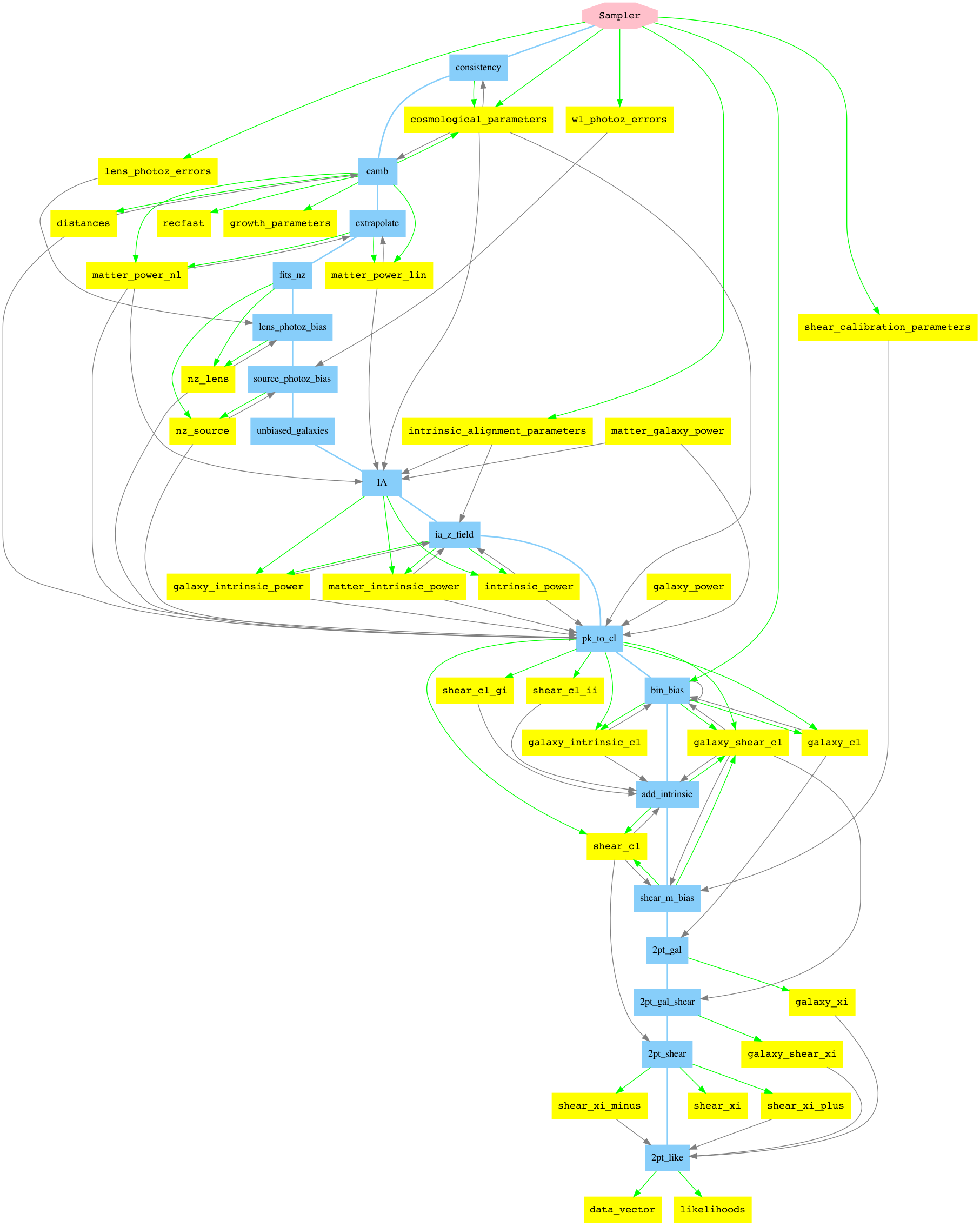
Making pipeline graphs¶
You will need the pygraphviz tool to use this feature. On Conda, you can install it with:
conda install -c conda-forge pygraphviz
Then you can create a graph from the command line using the --graph flag and then the graphviz dot command:
cosmosis --graph des-y1.dot examples/des-y1.ini
dot -Tpng -o des-y1.png des-y1.dot
And example is shown below:
Making a pipeline from a single likelihood function¶
New in version 3.3
If you have a single likelihood function that you want to use as a pipeline (so that you are really just using CosmoSIS for its sampling features), then you can do it like this:
import cosmosis
def log_like(x):
# your likelihood function here
return log_like
param_ranges = [
(-1.0, 0.0, 1.0),
# ...
# min, start, and max of each parameter of the likelihood
]
pipeline = cosmosis.LikelihoodPipeline.from_likelihood_function(log_like, param_ranges)
You can now test your pipeline, calling pipeline.posterior or pipeline.likelihood, or run a sampler like this:
sampler_config = {
"runtime": {
"sampler": "emcee",
"verbosity": "quiet",
},
"emcee": {
"walkers": 100,
# ... other emcee parameters
},
}
status, output = cosmosis.run_cosmosis(sampler_config, pipeline=pipeline, output='astropy')
The output will be an astropy table with the samples and likelihoods.
You can also use derived parameters or supply non-uniform priors. See the LikelihoodPipeline.from_likelihood_function docstring for details.